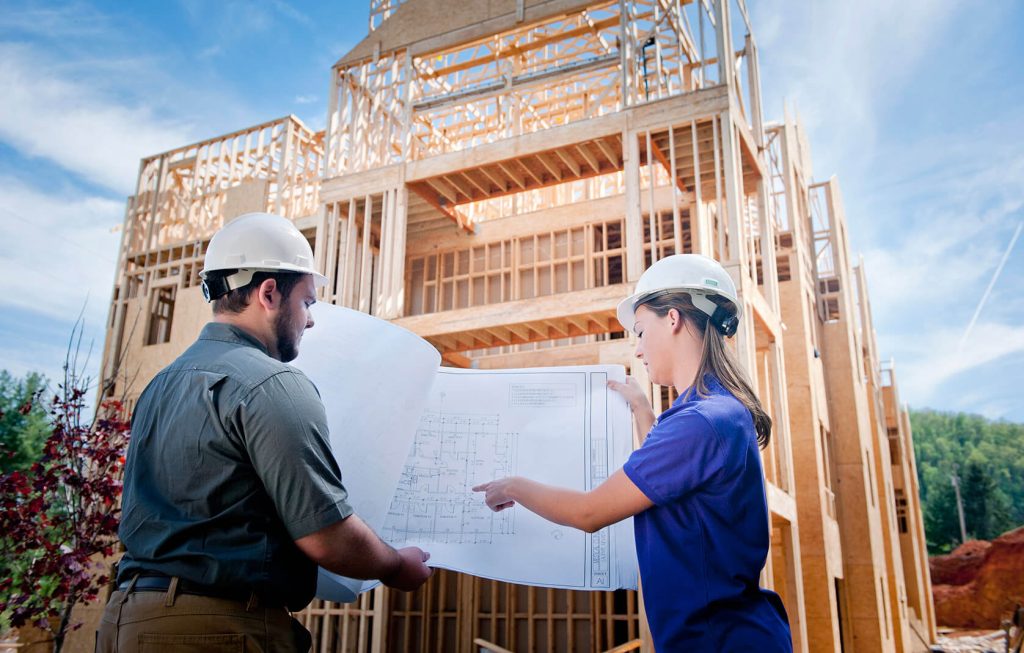
Bridge design and construction is a complex process that requires expertise in various fields, but none is more crucial than the role of a structural engineer. These professionals are responsible for ensuring that bridges are not only functional but also safe, durable, and aesthetically pleasing. This article delves into the essential responsibilities of structural engineers in the bridge-building process and highlights their critical contributions.
1. Design and Planning
The journey of a bridge begins with the design phase, where a structural engineer plays a pivotal role. During this stage, the structural engineer collaborates with architects, urban planners, and other engineers to create a design that meets the required specifications. They assess factors such as load-bearing capacities, environmental conditions, and material suitability. By using advanced software and modeling tools, the structural engineer can predict how the bridge will behave under various loads and stresses, ensuring that the design will be both functional and safe.
2. Material Selection
Choosing the right materials is essential for the longevity and stability of a bridge. The structural engineer evaluates different materials based on their strength, durability, and suitability for the specific environmental conditions. Whether it’s steel, concrete, or a combination of materials, the structural engineer ensures that the chosen materials will support the bridge’s weight and withstand environmental factors such as wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations.
3. Structural Analysis and Testing
Once the design is in place and materials are selected, the structural engineer conducts detailed analyses to ensure that the bridge will perform as expected. This involves using various analytical techniques and simulations to model the bridge’s behavior under different conditions. Structural engineers also oversee testing phases, where prototypes or components of the bridge are subjected to real-world conditions to verify their performance. This rigorous testing is crucial for identifying potential weaknesses and making necessary adjustments before the actual construction begins.
4. Construction Supervision
During the construction phase, the role of the structural engineer shifts to supervision and quality control. They work closely with construction teams to ensure that the bridge is built according to the approved design and specifications. The structural engineer monitors the construction process, checks materials, and verifies that all safety protocols are followed. Their expertise helps prevent potential issues that could arise during construction, ensuring that the bridge is completed on time and within budget.
5. Maintenance and Inspection
Even after a bridge is completed, the role of the structural engineer continues. Regular maintenance and inspections are vital to ensure the long-term safety and functionality of the bridge. The structural engineer develops maintenance schedules and inspection routines to detect any signs of wear and tear or structural issues. By addressing these concerns promptly, the structural engineer helps extend the bridge’s lifespan and prevent costly repairs or potential hazards.
6. Innovative Solutions
Structural engineers are also at the forefront of innovation in bridge design and construction. They explore new materials, technologies, and methods to improve bridge performance and sustainability. From incorporating renewable energy sources to developing advanced construction techniques, structural engineers constantly seek ways to enhance the efficiency and environmental impact of bridges.
Conclusion
In summary, the role of a structural engineer in bridge design and construction is multifaceted and critical to the success of any bridge project. From initial design and material selection to construction supervision and ongoing maintenance, structural engineers ensure that bridges are safe, functional, and enduring. Their expertise not only contributes to the structural integrity of bridges but also helps drive innovation in the field, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable infrastructure solutions.